Western Tamang - Nepali Dictionary
Tamang is a vibrant language spoken by the Tamang speech community. According to the 2011 Census of Nepal, Tamang ranks as the fifth most spoken language, with 5.1% of the population using it. It is a member of the Tibeto-Burman branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. The majority of Tamang speakers reside around the Kathmandu Valley, though the Tamang ethnic group is spread across various districts of Nepal. Recognizing its cultural significance, the Nepal government officially recognized Tamang as an indigenous ethnic community in 2058 VS. This recognition was further reinforced in the interim constitution of 2063 VS and the constitution of 2072 VS, which designate Tamang as a national language.
The 'Do:ra song' narrates the migration of Western Tamang people from Tibet into Nepal via 'Same' in the Himalayas. This migration has led to the establishment of Tamang communities in various locations such as 'Rhirhap', 'Gyagarden', below 'Bompo' and 'Lambu', and just above 'Same'. According to the traditions of Lama, Bompo, and Lambu, the northern part of the Earth is considered the tail and the southern part the head, influencing the Tamang practice of positioning the deceased's head towards the south before cremation. In Tamang culture, 'Sa' represents Earth and 'me' signifies Tail, thus 'Same' is viewed as 'the tail of the Earth'. The journey from the tail to the head is believed to bring many changes.
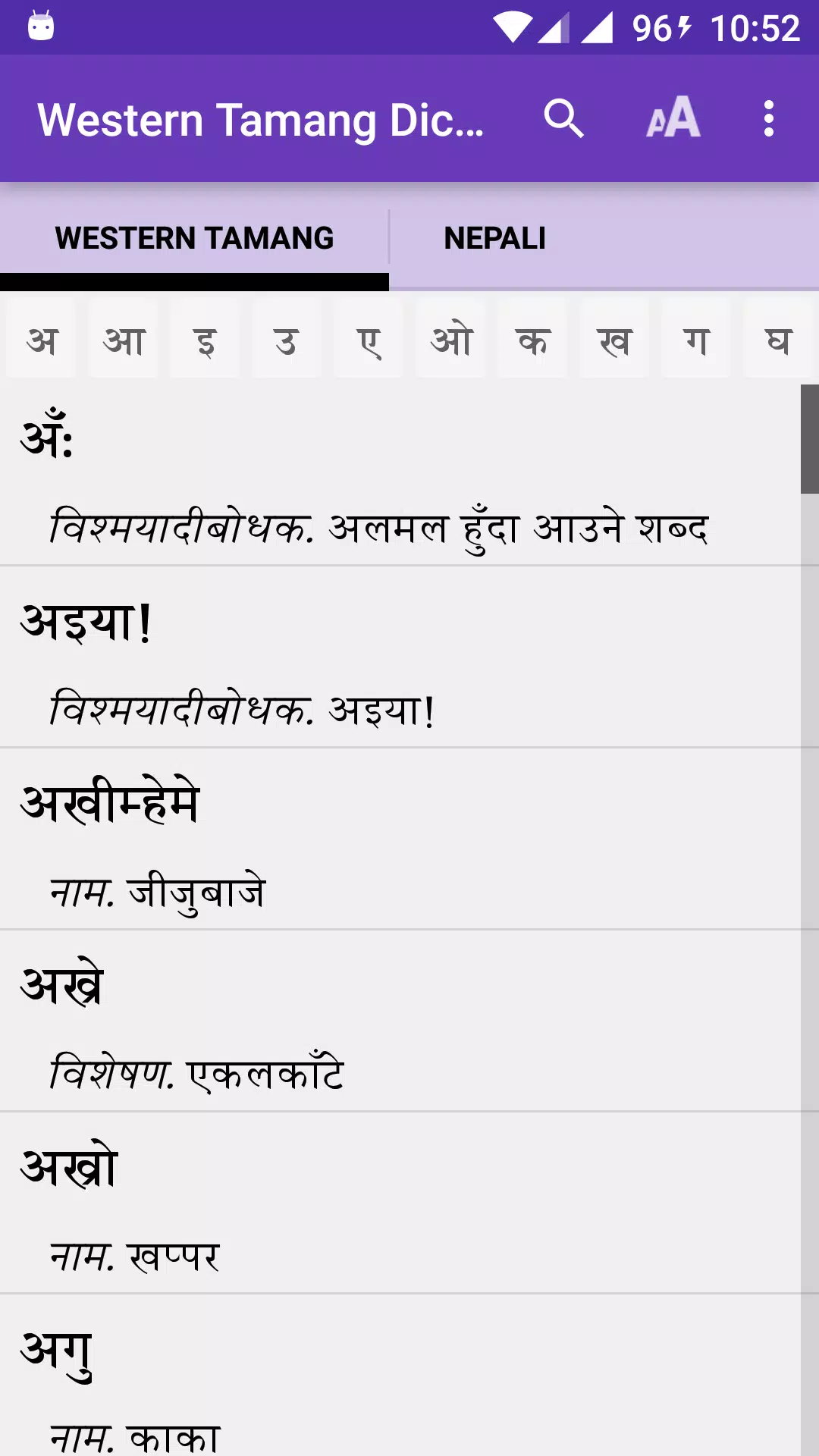
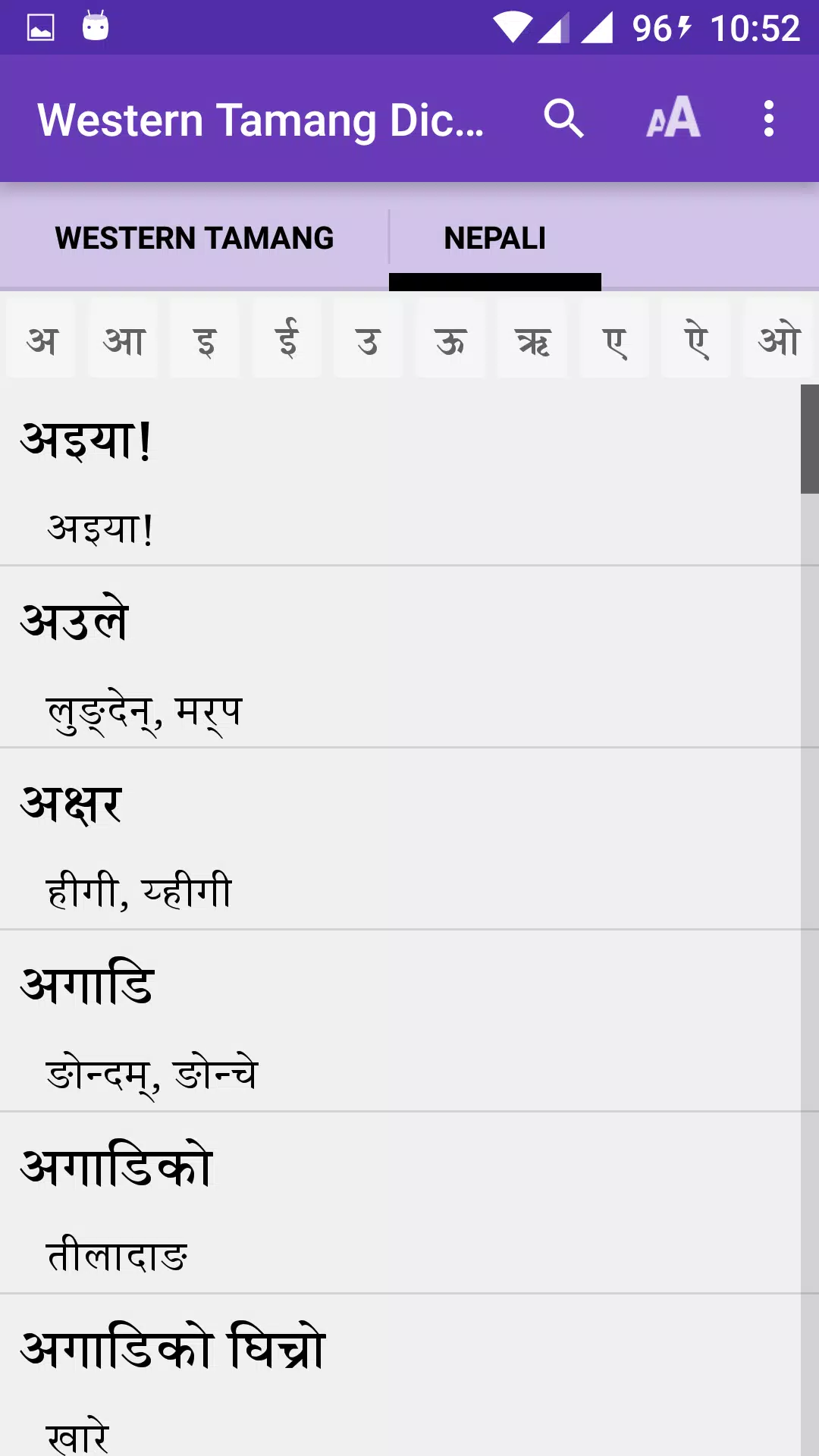
Tamang lacks a standardized grammar but is divided into two distinct dialects: Eastern and Western Tamang. Eastern Tamang, originating from the Langtang Himal and spoken east of the Trisuli River, is referred to as 'Syarba'. Western Tamang, spoken in districts like Rasuwa, Nuwakot, Dhading, Gorkha, Lamjung, Chitawan, and Kanchanpur, is known as 'Nhurba' or 'Nhuppa'.
This bilingual dictionary is a collaborative effort by members of the Western Tamang speech community from the aforementioned districts. Each Tamang word (source language) is translated into Nepali (target language), making it an invaluable resource for comparative linguistic studies. However, the number of Western Tamang speakers is declining due to the dominance of Nepali, the lingua franca. This shift poses a significant threat to the survival of Western Tamang as a mother tongue, highlighting the importance of this dictionary in the preservation, promotion, and development of the language.
Lastly, there is ample opportunity to enhance this dictionary further. The speech community, stakeholders, readers, organizations, and other concerned parties are encouraged to provide insightful comments and feedback for its continuous improvement.
What's New in the Latest Version 1.7
Last updated on Sep 29, 2024
- Updated on July 30, 2024
- New Android SDK